The future of China’s lithium battery industry is in Sichuan Province
With China’s largest reserves of lithium as well as an abundant supply of hydropower, China’s electric battery industry is migrating to the western province known for its spicy food.
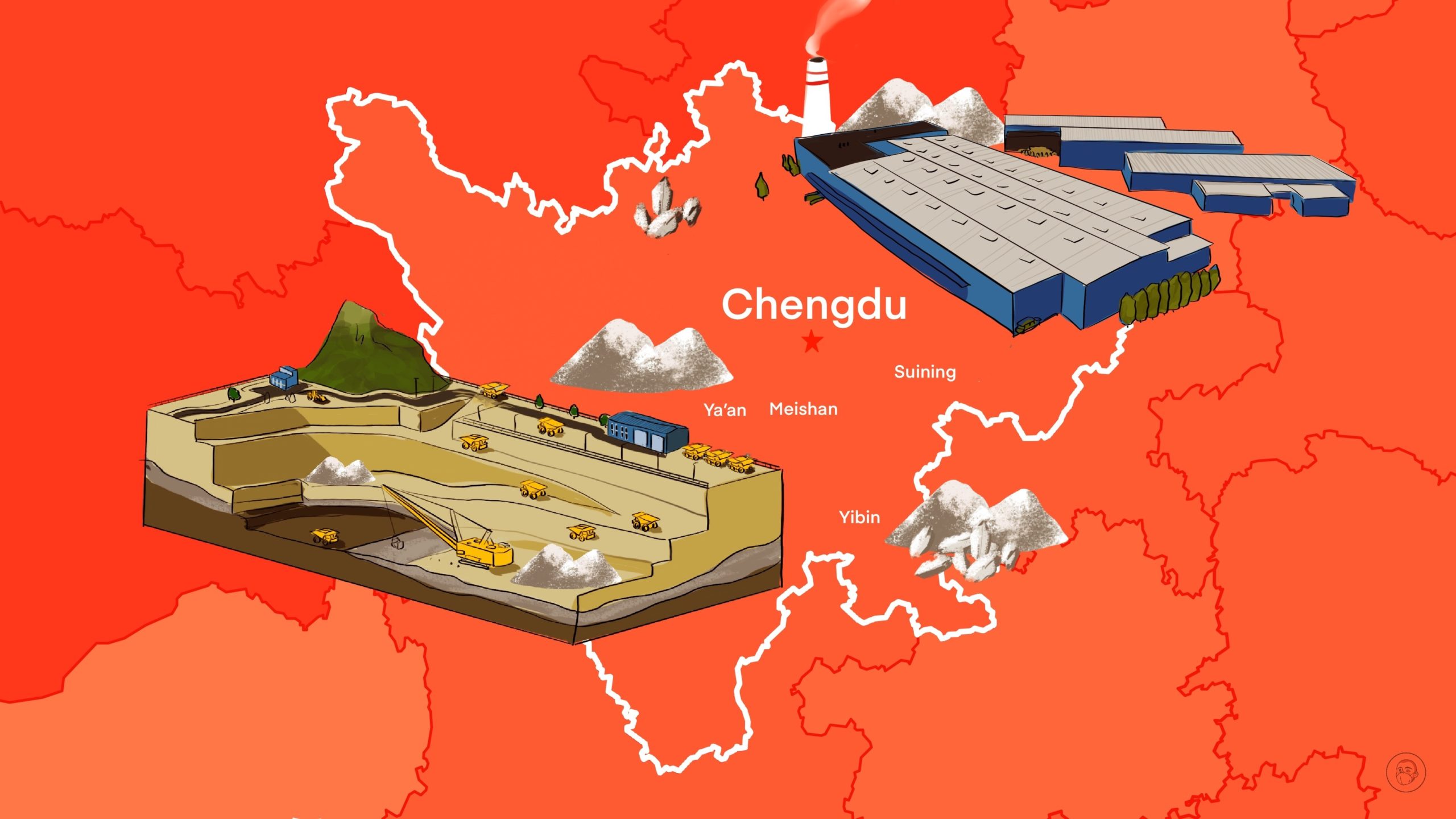
On September 23, the Sichuan provincial government issued a new plan for developing the province’s manufacturing industry. A key focus of the plan is electric batteries and the transformation of Sichuan into a world-class New Energy Vehicle (NEV) research and manufacturing base by 2027.
In fact, a westward migration of battery manufacturing from Shanghai, Jiangsu Province, and Zhejiang Province to Sichuan is already well underway:
In June 2021, CATL 宁德时代, China’s leading battery manufacturer, started operations at the first phase of the world’s largest single battery plant in the city of Yibin, Sichuan Province, which has a total investment of 64 billion yuan ($8.99 billion), and an annual capacity of 30 gigawatt hours (GWh). In addition to the plant, CATL also has facilities in Yibin for supplying lithium salts. In March 2022, this factory was certified as the world’s first zero carbon battery factory.
At the 2022 World Electric Vehicle and Electric Storage Battery Conference that took place in Yibin in July, the city government of Yibin signed 48 new contracts for projects related to battery and electric vehicle (EV) production, and for various related industries including cathode and anode materials, separators, electrolytes, copper foils, and battery recycling.
On July 30, 2022, CATL signed a framework agreement with the Chengdu provincial government for CATL to set up a regional research and development headquarters and research institute in Chengdu.
Several of China’s other leading battery companies have set up factories in Sichuan over the last few years, including Sunwoda Electronic 欣旺达, CALB 中创新航, Eve Energy 亿纬锂能 (with a battery production base of 20 billion yuan/$2.80 billion), and SVOLT 蜂巢能源. Most recently, on September 21 this year, CHAM Battery 创明新能源 signed an agreement of 12 billion yuan ($1.68 billion) to construct a battery cell production base in the city of Mianyang.
China news, weekly.
Sign up for The China Project’s weekly newsletter, our free roundup of the most important China stories.
A tale of two cities
While Yibin has become the focus area for battery production, the city of Suining has become the focus area for the processing of lithium battery materials.
A full ecosystem for lithium resource development and battery recycling has been established in Suining, with 52 lithium battery-related industrial enterprises. In 2021, the revenue of Suining’s lithium battery industry increased by 67.3%, and the total planned investment of lithium battery projects in the town exceeds 60 billion yuan ($8.42 billion).
Lots of lithium and cheap hydropower
According to data by a Chinese research institute, in 2021, East China (including the Yangtze River Delta) accounted for 60% of China’s battery production, with an output of 300 GWh, while southwest China, including Sichuan province, only accounted for 12%. But with all the new battery capacity being newly established in Sichuan, according to the institute, the battery production capacity of southwest China is going to catch up fast, and is expected to reach 350 GWh by 2025.
The main reason for Sichuan’s attractiveness for battery manufacturers is lithium: Sichuan has 6.1% of the world’s and 57% of China’s lithium ore reserves. According to one estimate, by 2025, Sichuan will have a total lithium mining capacity of five million tons and a lithium salts production capacity of 600,000 tons. Given the extremely high cost of the raw materials necessary for battery production and the vertical integration currently underway in the industry, Sichuan’s large lithium reserves make the province a natural choice for the battery makers .
Another key advantage for Sichuan is abundant clean energy, which is a particular advantage for the high energy consumption required for manufacturing batteries. With seven of China’s largest ten hydropower plants, Sichuan has hydropower capacity exceeding 90 million kilowatts, and the proportion of clean energy is as high as 80%.
CATL was able to build a huge zero carbon battery plant in Yibin because 73.5% of the city’s power is based on hydropower, and more than 80% of the plant’s energy is based on renewable energy. Sichuan’s energy, moreover, is not only more abundant but also cheaper than in east China.






